Category: Uncategorized
-
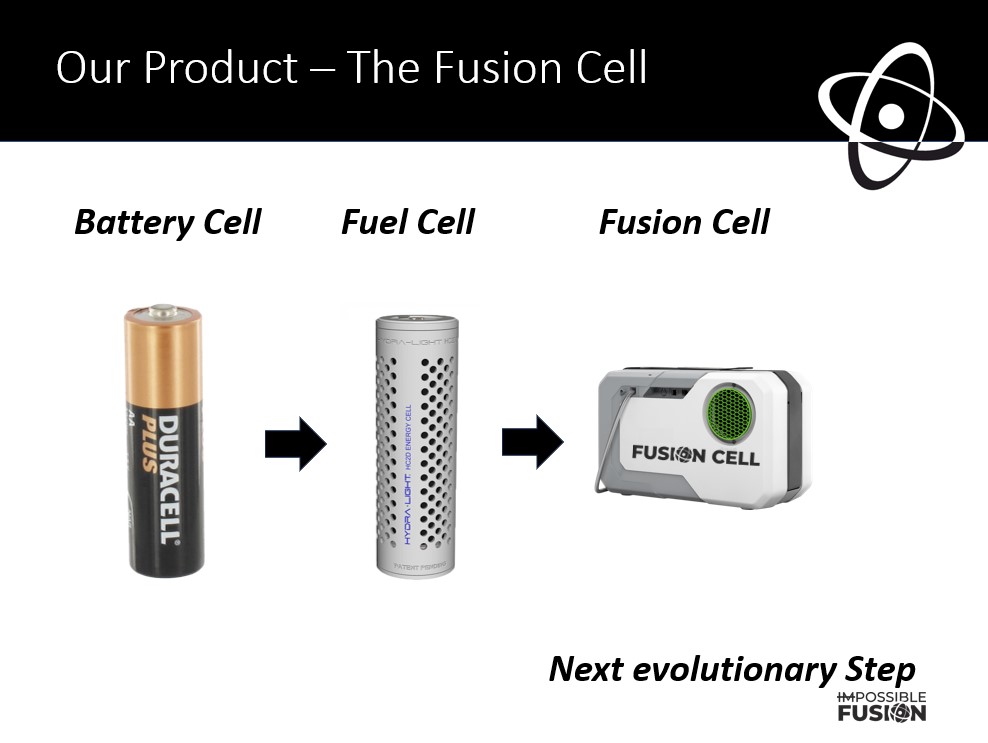
From Battery Cell to Hydrogen Fuel Cell to Heavy Water Fusion Cell: A Trajectory of Energy Density and Power Potential
The evolution of energy technologies reflects humanity’s enduring quest to store and release energy more densely, cleanly, and efficiently. From the humble battery cell powering a flashlight to the tantalizing promise of heavy water fusion, each step represents a leap in how we harness and release stored energy. At the heart of this progression lies
-
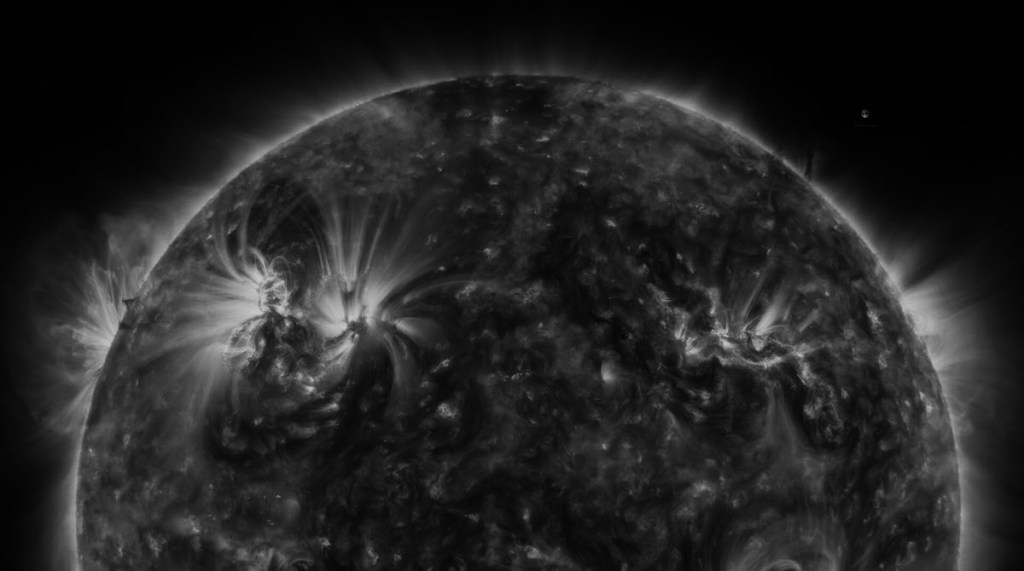
Nuclear Fusion in Germany
In the future, fusion energy is expected to provide clean, safe, and resource-efficient electricity regardless of weather conditions. There is still a long way to go, but the race to build the first fusion power plant is in full swing. The German government has set itself the goal of building the world’s first fusion power
-

FUSION CELL Trademark
Owning a FUSION CELL trademark as a brand means having the exclusive legal right to use the name “FUSION CELL” to identify and distinguish one’s products or services from those of others in the marketplace. This provides both brand protection and market advantages within the product or service classes covered by the trademark registration. Trademark
-

Hot vs. Cold Fusion
Cold Fusion & Hot Fusion – The Differences The table highlights key distinctions between hot and cold fusion, thereby clarifying what cold fusion is not: It does not operate at millions of degrees Celsius, does not require high-energy particle collisions in plasma reactors, and does not need extremely high energy inputs. Attributes
-

The Fusion Cell
A Fusion Cell in the context of cold fusion and nuclear science is an electrochemical device designed to create the conditions for possible nuclear fusion reactions at or near room temperature—commonly referred to as “cold fusion”. Core Design and Setup Experimental Goals and Principles Schematic Description Experimental Issues In summary, a Fusion Cell for cold
-

Summary of the ICCF‑26 conference
ICCF 26 served as a dynamic platform for sharing the latest experimental findings and theories in LENR.
-
Vielversprechende wissenschaftliche Ansätze in der aktuellen Forschung zur Kalten Fusion
Artikel mit vielversprechenden wissenschaftlichen Ansätze in der aktuellen Forschung zur Kalten Fusion.
-

Why hot fusion may never work
Scientists differentiate between hot fusion and cold fusion. Hot fusion is trying to bring the sun down to earth. Hot fusion requires temperatures of up to 150.000.000 degree celsius (ITER reactor), extrem vacuum or pressure and very strong magnetic fields. The aim is to bring hydrogen atoms or its isotops so close together that they